

Specify the Recordset Structure giving the list of nodes including the root and substructure that needs to be read. File Content Conversion comes in handy here. File Content Conversion in Receiver AdapterĪssume you have XML content as generated by the sender adapter above and are required to generate a tab-separated file (as shown in the below figure) at the receiver end. fieldNames – list of field names in each record.įor an exhaustive list of parameters available for record set structure please go through this link. endSeparator – signifies the end of a record, ‘nl’ (including quotes) indicates a new line character.
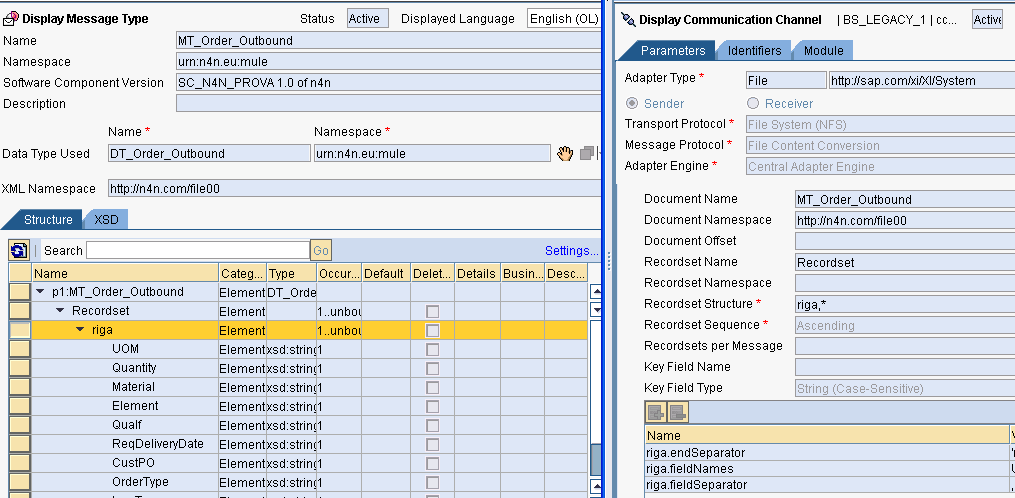
for a tab-separated file, you could provide ‘0x09’ (including quotes). fieldSeparator – can be a comma for a CSV file or any other separator. Three mandatory parameters that must be provided are – In our case ‘Emp,*’ indicates that node Emp can occur any number of times within the root node. In Recordset Structure you specify the substructure and its occurrence. If you don’t specify this, PI creates a default root node called Recordset. This should be in sync with the message structure in the Integration Repository.

Recordset Name specifies the name of the root node that should be created while generating the corresponding XML. The figure below shows a typical configuration for the sender adapter.ĭocument Name and namespace indicate the message type used (from the Integration Repository).
Let’s say we have a simple CSV (Comma-separated values) file something like the one shown in the below figure. File Content Conversion in Sender Adapter Here we will understand how to use File Content Conversion (FCC) in sender & receiver file adapter. File Content Conversion helps in converting the file formats to/from XML. In this article, we will understand the concept of File Content Conversion in SAP PI using an example of a comma-separated text file as source.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
